Topical Pain Relief Comparison Tool
Emulgel (Diclofenac)
- Active Ingredient: Diclofenac
- Onset Time: 30-45 minutes
- Best For: Joint and muscle aches
- Side Effects: Mild skin irritation
- Cost: Moderate
Ibuprofen Gel
- Active Ingredient: Ibuprofen
- Onset Time: 20-30 minutes
- Best For: Sports injuries
- Side Effects: Minimal skin irritation
- Cost: Low-Moderate
Ketoprofen Gel
- Active Ingredient: Ketoprofen
- Onset Time: 20-30 minutes
- Best For: Tendinitis/bursitis
- Side Effects: More skin irritation
- Cost: Moderate-High
Capsaicin Cream
- Active Ingredient: Capsaicin
- Onset Time: Several days
- Best For: Chronic pain
- Side Effects: Burning sensation
- Cost: Low
Lidocaine Patch
- Active Ingredient: Lidocaine
- Onset Time: Immediate
- Best For: Nerve pain
- Side Effects: Minimal
- Cost: High
Menthol Rub
- Active Ingredient: Menthol
- Onset Time: Immediate
- Best For: Temporary relief
- Side Effects: Minimal
- Cost: Very Low
Decision Factors:
- Cost: Menthol rub is cheapest; lidocaine patches are most expensive
- Onset Time: Menthol and lidocaine provide immediate relief; capsaicin takes several days
- Side Effects: Diclofenac and ketoprofen may cause skin irritation; others have minimal side effects
Choose based on your specific pain type, budget, and tolerance for potential side effects.
Quick Takeaways
- Emulgel contains diclofenac, a potent NSAID that works within 30‑45 minutes for joint and muscle aches.
- Ibuprofen gel and ketoprofen gel offer similar anti‑inflammatory effects but differ in skin irritation risk.
- Capsaicin cream and menthol rub provide pain‑blocking sensations without systemic absorption.
- Lidocaine patches are ideal for nerve‑related pain where anti‑inflammatories are less effective.
- Cost, onset time, and side‑effect profile are the three main decision factors.
What Is Emulgel?
When treating localized pain, Emulgel is a topical gel that delivers the non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drug (NSAID) diclofenac directly to the skin. It was launched in the UK in the early 2000s and quickly became a go‑to for athletes and anyone with a sore knee, sprained ankle, or lower‑back strain. The gel base helps the active ingredient penetrate the dermis, reaching inflamed tissues without the gastrointestinal side effects of oral diclofenac.
How Diclofenac Works Inside the Gel
Diclofenac belongs to the arylacetic acid class of NSAIDs. It blocks cyclooxygenase‑2 (COX‑2) enzymes, which reduces prostaglandin production-the chemicals that trigger swelling and pain. By applying it topically, the drug concentration stays high where it’s needed, while blood‑level exposure stays low, limiting systemic risks.
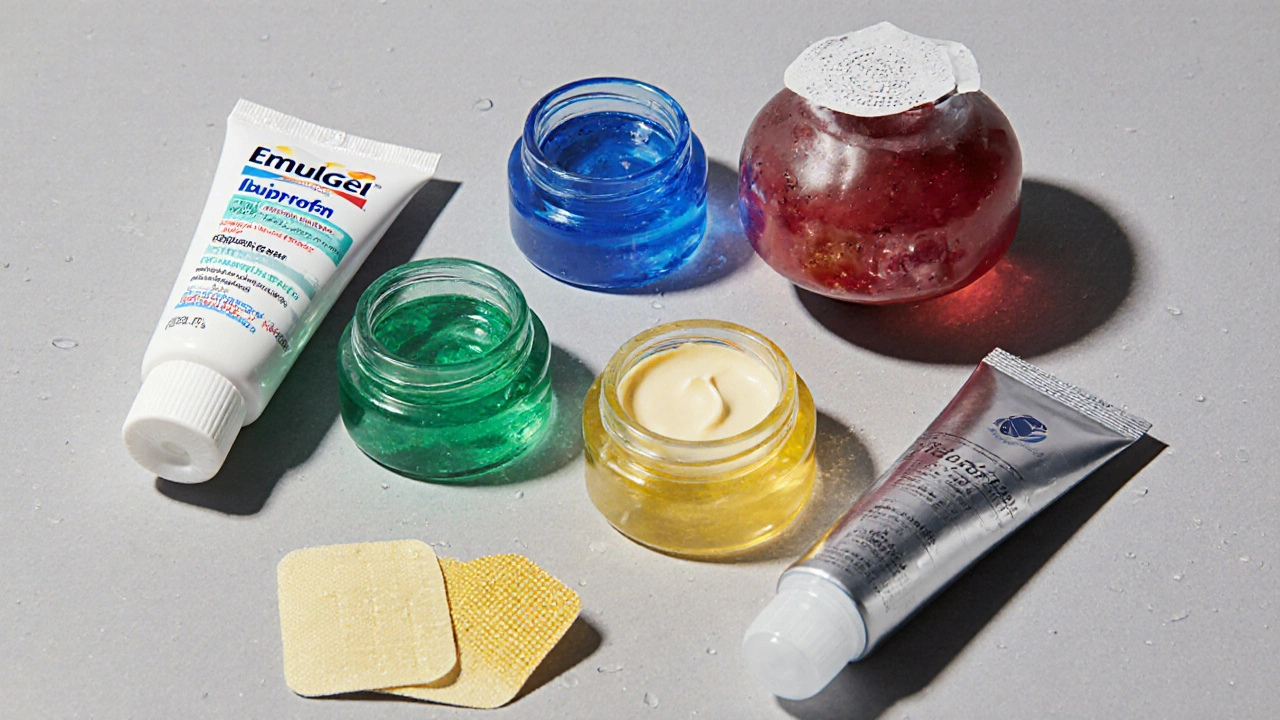

Topical Alternatives to Emulgel
Several other topical agents compete for the same market. Below are the most common ones you’ll see in UK pharmacies.
Ibuprofen gel is a gel formulation that contains ibuprofen, another NSAID with a slightly shorter half‑life than diclofenac. It typically starts working within 20‑30 minutes and is marketed for fast relief of sports injuries.
Ketoprofen gel is a topical NSAID that penetrates deeply into tendons and ligaments, making it popular for tendinitis and bursitis. Its onset is similar to ibuprofen, but some users report more skin irritation.
Capsaicin cream is a dermal preparation derived from hot peppers that depletes substanceP, a neurotransmitter involved in pain signaling. It doesn’t act as an anti‑inflammatory; instead, it creates a burning sensation that desensitizes nerves over several days of use.
Lidocaine patch is a self‑adhesive patch delivering the local anesthetic lidocaine directly to the skin. It’s most effective for post‑herpetic neuralgia or localized nerve pain, providing up to 12hours of numbness.
Menthol rub is a cooling agent that activates TRPM8 receptors, giving a soothing, counter‑irritant effect. It’s non‑medicinal but often combined with NSAIDs for a dual‑action feel.
Side‑Effect Snapshot
All topicals carry a risk of skin reactions, but the systemic profile varies.
- Emulgel - mild erythema in <5% of users, rare systemic NSAID effects.
- Ibuprofen gel - slightly higher incidence of dermatitis, especially on sensitive skin.
- Ketoprofen gel - up to 8% report itching or burning.
- Capsaicin - initial burning is expected; tolerance builds after 3‑5 days.
- Lidocaine patch - occasional local numbness and allergic rash.
- Menthol - transient cooling and mild redness, no serious adverse events.
Cost Comparison (UK 2025)
| Product | Active ingredient | Typical dose | Onset | Duration | Avg UK price (2025) | Key side‑effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulgel | Diclofenac 1% | Apply 2‑4g to affected area 3‑4×/day | 30‑45min | 6‑8h | £7.99 for 30g tube | Mild skin irritation |
| Ibuprofen gel | Ibuprofen 5% | 2‑3g 3‑4×/day | 20‑30min | 4‑6h | £6.50 for 25g tube | Dermatitis |
| Ketoprofen gel | Ketoprofen 2.5% | 2‑4g 3‑4×/day | 30‑45min | 6‑8h | £8.20 for 30g tube | Itching, burning |
| Capsaicin cream | Capsaicin 0.025‑0.075% | Thin layer 3‑4×/day | 1‑2h (burn first) | 8‑12h | £9.00 for 30g tube | Burning, erythema |
| Lidocaine patch | Lidocaine 5% | One 5cm×5cm patch | 15‑30min | Up to 12h | £12.50 per patch | Local numbness, rash |
| Menthol rub | Menthol 10% | Apply thinly as needed | Immediate | 1‑2h | £5.30 for 20g tube | Redness, tingling |
Choosing the Right Topical for Your Situation
Three variables usually decide which product wins: the type of pain, skin sensitivity, and how quickly you need relief.
- Acute joint or muscle strain: Emulgel or ibuprofen gel give the fastest anti‑inflammatory flare‑up control. Emulgel edges out ibuprofen for deeper joint penetration.
- Chronic tendon or bursitis pain: Ketoprofen’s higher lipophilicity helps it sit in tendons longer, but if you have eczema‑prone skin, the safer route is Emulgel.
- Nerve‑related or post‑herpetic pain: Lidocaine patches provide localized numbness without any anti‑inflammatory action.
- Heat‑sensitive or sensitivity to chemicals: Menthol rub or a low‑percentage capsaicin cream can give a soothing feeling without the risk of NSAID‑related gastrointestinal warnings.
When cost is a major factor, Emulgel remains one of the cheapest NSAID gels that still offers a solid therapeutic window.
Practical Tips & Safety Precautions
- Wash and dry the area before application; residual soap can block absorption.
- Use a pea‑size amount per 10cm²; more does not mean faster relief and can increase irritation.
- Avoid covering the gel with airtight dressings unless a doctor advises it.
- Never apply on broken skin, open wounds, or directly onto mucous membranes.
- If you’re on oral NSAIDs or anticoagulants, consult a pharmacist before adding a topical NSAID.
For pregnant or breastfeeding women, topical NSAIDs are generally discouraged after the first trimester; seek professional advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use Emulgel together with oral diclofenac?
Combining both routes usually raises the risk of systemic side effects without adding extra pain relief. Keep to one form unless a doctor specifically prescribes a combined regimen.
How long should I keep using a topical NSAID?
Most guidelines suggest a maximum of 7‑10days for acute injuries. For chronic conditions, rotate products every few weeks to lower skin‑irritation risk.
Is Emulgel safe for children?
In the UK, Emulgel is licensed for patients aged 12years and older. For younger children, consult a paediatrician before any NSAID use.
What should I do if I develop a rash after applying a gel?
Stop using the product immediately, wash the area with mild soap, and apply a soothing emollient. If the rash persists or spreads, seek medical attention.
Are topical NSAIDs as effective as oral ones?
For localized pain, topicals can match oral NSAIDs in pain reduction while avoiding stomach irritation. They are less effective for widespread inflammation or fever.





17 Comments
Robert Brown
October 10, 2025 AT 14:37 PMEmulgel is overrated, just a cheap NSAID masquerading as a miracle.
Erin Smith
October 11, 2025 AT 07:17 AMHonestly, it does the job for a lot of folks. If you need quick relief, give it a shot.
George Kent
October 11, 2025 AT 23:57 PM🇬🇧 Stop whining about a British staple!!! It works fine!!! 🤬💥
Jonathan Martens
October 12, 2025 AT 16:37 PMThe pharmacokinetic profile of the diclofenac gel, when applied topically, circumvents first-pass metabolism-so you get localized COX-2 inhibition without the gastric fallout. Nice, huh?
Jessica Davies
October 13, 2025 AT 09:17 AMOne would assume that a mere topical NSAID could rival the nuanced neuromodulation of lidocaine patches, yet the literature suggests otherwise-an oversight perpetuated by commercial hype.
Kyle Rhines
October 14, 2025 AT 01:57 AMIt is noteworthy that the major pharmaceutical conglomerates have synchronized the release dates of these gels to maximize market saturation-a coordinated strategy, not mere coincidence.
Lin Zhao
October 14, 2025 AT 18:37 PMGreat rundown! I’ve tried both Emulgel and the menthol rub, and the combo actually feels smoother on sore knees :)
Laneeka Mcrae
October 15, 2025 AT 11:17 AMEmulgel’s diclofenac concentration is calibrated to penetrate the dermis efficiently, delivering anti-inflammatory action within half an hour. Compared to ibuprofen gel, the onset is marginally slower but the duration of effect tends to be longer. The side‑effect profile is modest-mostly mild erythema, which is acceptable for short‑term use. Costwise, it sits in the moderate range, making it accessible without breaking the bank. For athletes with joint pain, the gel’s non‑systemic nature is a significant advantage over oral NSAIDs. However, patients with sensitive skin should patch test before full application. The guide correctly highlights that lidocaine patches, while pricey, excel for neuropathic pain where NSAIDs fall short. On the other hand, menthol rubs provide instant cooling but lack anti‑inflammatory benefits. Ultimately, the choice hinges on whether you prioritize rapid onset, depth of penetration, or budget constraints.
Kendra Barnett
October 16, 2025 AT 03:57 AMHey, that’s a solid summary! If you’re on a tight budget, the menthol rub can be a decent stop‑gap while you hunt for a prescription.
Warren Nelson
October 16, 2025 AT 20:37 PMGood points all around. I’d add that the gel’s vehicle-usually a hydro‑alcoholic base-helps with absorption but can sting a bit on cracked skin. Some users report that layering a thin moisturiser after the gel reduces that sensation without diluting efficacy. Also, rotating between diclofenac and ibuprofen gels can prevent tolerance buildup.
Jennifer Romand
October 17, 2025 AT 13:17 PMIn the grand theater of pain relief, Emulgel plays the understudy while the lidocaine patch steals the spotlight-truly a tragic miscast.
Kelly kordeiro
October 18, 2025 AT 05:57 AMThe comparative analysis of topical analgesic modalities warrants a meticulous exposition that transcends superficial marketing rhetoric.
Diclofenac, the active moiety in Emulgel, operates as a non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory agent by selectively inhibiting the cyclooxygenase‑2 isoenzyme, thereby attenuating prostaglandin synthesis at the site of inflammation.
Its pharmacodynamic profile, when delivered via a gel matrix, affords a localized concentration gradient that surpasses that achieved by oral administration, whilst concomitantly mitigating systemic exposure.
Conversely, ibuprofen gel, though sharing a similar mechanistic pathway, exhibits a comparatively abbreviated half‑life and necessitates more frequent reapplication to sustain analgesia.
Ketoprofen gel, positioned at the higher end of the cost spectrum, has been documented to induce a heightened incidence of dermal irritation, an adverse effect attributable to its intrinsic physicochemical properties.
Capsaicin cream, derived from Capsicum species, eschews anti‑inflammatory action in favour of nociceptor desensitization through substance P depletion, a process that mandates prolonged, daily application before clinically appreciable relief emerges.
Lidocaine patches, embodying a class of local anesthetics, achieve immediate neuronal blockade by stabilising the neuronal membrane and impeding sodium influx, rendering them particularly efficacious for neuropathic pain syndromes.
Menthol rubs, while devoid of pharmacologic activity beyond counter‑irritation, exploit the activation of transient receptor potential melastatin‑8 channels to evoke a cooling sensation that transiently distracts from underlying nociception.
The economic considerations are non‑trivial; menthol preparations represent the most economical option, whereas lidocaine patches command a premium price reflective of their sophisticated delivery system.
From a clinical decision‑making perspective, the practitioner must appraise the etiological nature of the pain, the temporal urgency of relief, and the patient’s cutaneous tolerance.
Patients with acute musculoskeletal strain may derive sufficient benefit from Emulgel or ibuprofen gel, given their modest onset latency and anti‑inflammatory potency.
In contrast, chronic neuropathic pain, such as post‑herpetic neuralgia, is more amenable to lidocaine patches, whose anesthetic action directly targets ectopic nerve firing.
The aforementioned side‑effect profiles underscore the necessity for a thorough skin assessment prior to initiation of any topical regimen.
Furthermore, the potential for systemic absorption, albeit minimal, should be contemplated in patients with comorbidities such as hepatic insufficiency.
It is incumbent upon the prescriber to elucidate the proper application technique, including the recommended dosage, frequency, and duration, to optimise therapeutic outcomes.
In summation, the selection of an appropriate topical analgesic is a nuanced endeavour that amalgamates pharmacologic efficacy, safety, cost, and patient preference.
Chris Fulmer
October 18, 2025 AT 22:37 PMI appreciate the thoroughness of the guide; it gives a clear roadmap for anyone navigating the crowded market of topicals.
Larry Douglas
October 19, 2025 AT 15:17 PMThe presented data aligns with current pharmacopeial standards and offers actionable insight for clinicians
Michael Stevens
October 20, 2025 AT 07:57 AMGreat job breaking down the options-this will help a lot of people pick the right product for their pain.
Ann Campanella
October 21, 2025 AT 00:37 AMThis guide is half‑baked.
Desiree Tan
October 21, 2025 AT 17:17 PMDon’t overthink it-Emulgel gives the relief you need, so stick with it.