Topical NSAIDs: Fast Relief for Pain and Inflammation
When it comes to Topical NSAIDs, medicines you apply to the skin to cut pain and swelling without swallowing a pill. Also known as topical nonsteroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs, they have become a go‑to for anyone dealing with sore joints, bruised muscles, or minor injuries. topical NSAIDs let the drug act right where it’s needed, keeping the rest of your body out of the equation.
Broadly, NSAIDs, a class of drugs that reduce inflammation by blocking prostaglandin production work systemically when taken by mouth, but the skin‑applied versions stay localized, lowering the risk of stomach upset. The most common active ingredient you’ll see on the label is diclofenac, a potent anti‑inflammatory that penetrates skin to reach the underlying tissue. Other topical options include ibuprofen gel, ketoprofen cream and naproxen patches. These products share a core idea: Topical NSAIDs encompass diclofenac gels, ibuprofen creams, and similar formulations, offering a range of strengths for different needs.
People use these gels, creams, or patches to tackle musculoskeletal pain, discomfort arising from muscles, tendons, ligaments or joints. Whether you’re nursing a tennis elbow, a sore knee from hiking, or an arthritis flare‑up, a thin layer of gel can deliver relief in minutes. The skin acts as a delivery system, so Topical NSAIDs require proper skin preparation – clean, dry, and free of cuts – to maximize absorption. A quick rub before bedtime can keep you moving the next day without the systemic side effects of oral pills.
When They Shine and What to Watch For
These products shine in short‑term situations: sprains, strains, tendinitis, and mild to moderate osteoarthritis. Because the drug stays near the site of injury, Inflammation influences the effectiveness of topical NSAIDs – more swelling can actually help the medication seep deeper. However, they’re not a cure‑all. Large open wounds, severe skin conditions, or allergies to the active ingredient call for a different approach. Also, people on anticoagulants should check with a doctor before using a diclofenac patch, as it can increase bleeding risk under the skin.
Below you’ll find a hand‑picked collection of articles that dive deeper into specific drugs, compare alternatives, and give practical buying tips. From beta‑blocker comparisons to guides for safe online purchases of generic medicines, the list covers a wide range of medication topics that often intersect with pain management and inflammation control. Browse the posts to see how topical NSAIDs fit into broader treatment plans, learn about alternative pain relievers, and pick the right option for your situation.
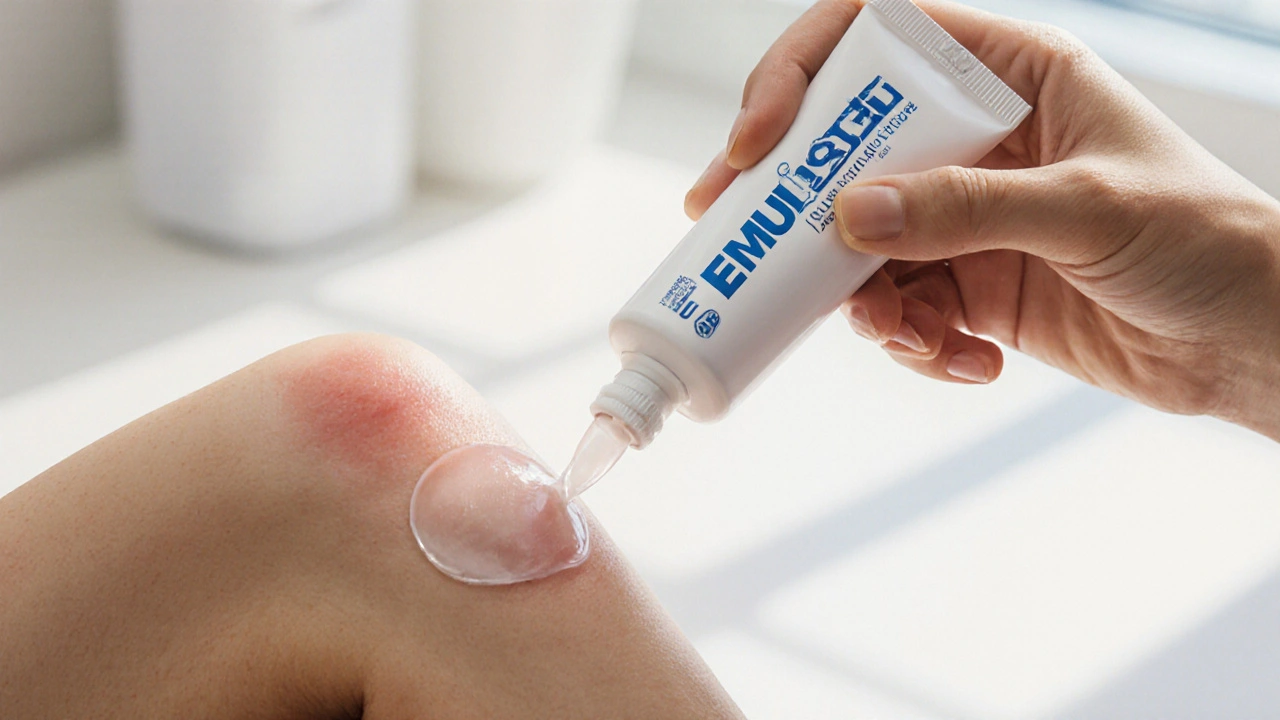
Emulgel (Diclofenac) vs Topical Pain Relief Alternatives - Comparison Guide
A clear, side‑by‑side comparison of Emulgel (diclofenac) with other topical pain relief options, covering effectiveness, cost, safety and best‑use scenarios.